Information for Teachers
Curriculum links
This investigation is linked to the following Grade 5 Next Generation Science Standards.
LS2.A: Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems
The food of almost any kind of animal can be traced back to plants. Organisms are related in food webs in which some animals eat plants for food and other animals eat the animals that eat plants. Some organisms, such as fungi and bacteria, break down dead organisms (both plants or plants parts and animals) and therefore operate as “decomposers.” Decomposition eventually restores (recycles) some materials back to the soil. Organisms can survive only in environments in which their particular needs are met. A healthy ecosystem is one in which multiple species of different types are each able to meet their needs in a relatively stable web of life. Newly introduced species can damage the balance of an ecosystem. (5-LS2-1)
ESS3.C: Human Impacts on Earth Systems
Human activities in agriculture, industry, and everyday life have had major effects on the land, vegetation, streams, ocean, air, and even outer space. But individuals and communities are doing things to help protect Earth’s resources and environments. (5-ESS3-1)
How to search the internet
1 Keep your request short
Fewer words will give a more accurate search.
2 Choose exactly what you want
For example: Arctic Circle Climate
3 Use quotes
Double quotes around a set of words tell the search engine to consider those exact words in that exact order without any change. For example: “Arctic Circle Climate”
4 Use the plus sign (+)
If you add a plus sign (+) between words, the internet will search for all the words. For example: migrate+birds+whales+mammal
5 Use the minus sign (–) to say what you don’t want
Use a minus sign (–) to show words you do not want to appear in your results. For example: if you search for burrowing animals and do not want mammals in your search, –mammals will exclude mammals. Note that you need to put a space before the minus sign for the word to be excluded.
6 Be very clear about what you don’t want
Part 1
Ask questions and define problems
After reading Sharing the Environment, you may have many questions about how people share our planet with wild animals.
List your questions
- Compare your list with questions that others have.
- Choose a question you would like to investigate.
- You can work alone, with a partner, or in a small group.
You may want to choose one or more of these questions to investigate
Q1. How has human activity had an impact on the availability of some animals’ habitats?
Q2 Why are some animals in danger of dying out?
Q3 What is being done to help these animals?
Go to Part 2 Investigate →Part 2
Investigate
Do searches in the internet or in books or talk to people who can help to find the information you are looking for.
Your teacher may suggest suitable websites for further information.
Go to Part 3 Record data →Part 3
Record data
Find a way of recording your information that will allow you to see any patterns in the data.
Data Chart for Sharing the Environment
[Download and change to suit your information]
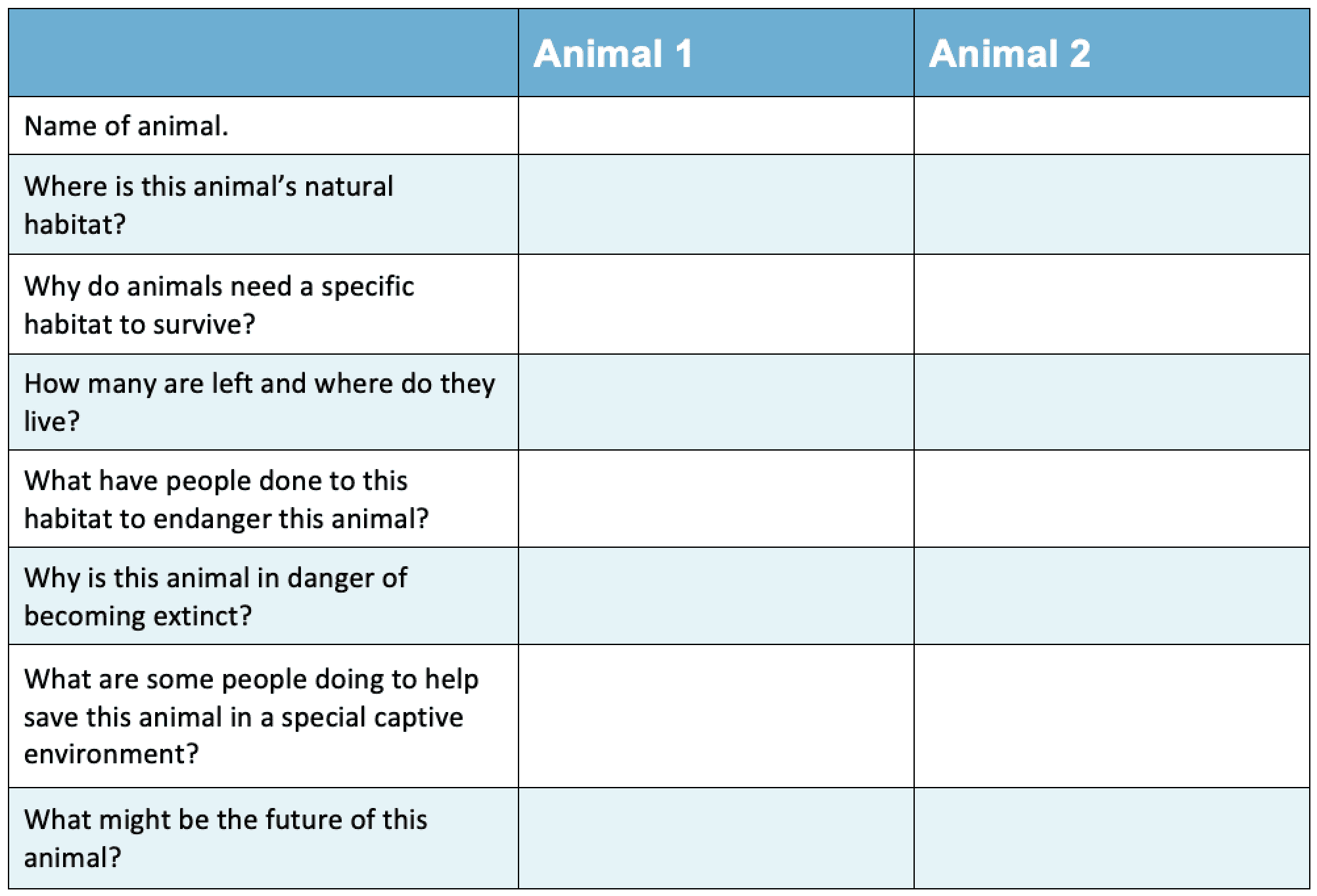 Download Chart
Download Chart
Go to Part 4 Organize, analyze, and interpret data →
Part 4
Organize, analyze, and interpret data
1. Look over the information you have gathered and the patterns you have found.
What do all animals need to survive?
What has threatened some animals’ ability to survive in the wild?
2. Search for other patterns.
Why is it a concern that this animal is in danger of becoming extinct?
How are groups around the world working together to save the habitats of these animals?
What might happen to these habitats in the future?
How can they be protected?
3. Makes notes about what you find.
Go to Part 5 Present and share →Part 5
Present and share
Look over all of the information that you have gathered in your investigation.
What are the most important ideas about sharing the environment with wild animals?
Make a chart showing the most important ideas.
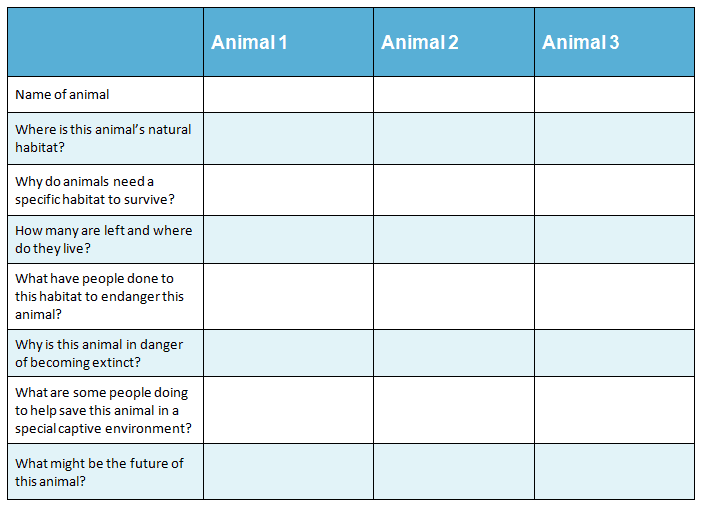 Download Chart
Download Chart
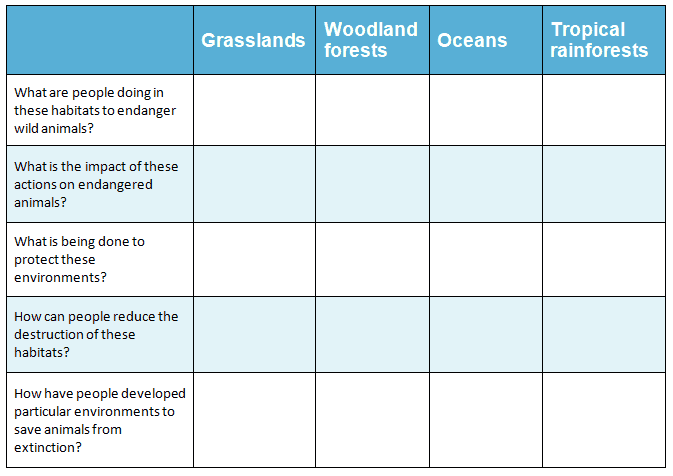 Download Chart
Download Chart
← Return to menu